//users/33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8/ratecard/501703411_1220588246528028_2433991182366402613_n.jpg)
%2Ffit-in%2F300x300%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fratecard%2F501703411_1220588246528028_2433991182366402613_n.jpg&w=256&q=75)
%2F300x300%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fstriped-bass-fishing-oxford-2678.jpeg&w=256&q=75)
%2F300x300%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fsix-bluefish-oxford-fishing-2624.jpeg&w=256&q=75)
%2F300x300%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fstriped-bass-fishing-md-2633.jpeg&w=256&q=75)
%2F300x300%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fstriped-bass-fishing-oxford-2701.jpeg&w=256&q=75)
%2F300x300%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Ffishing-adventure-oxford-2495.jpeg&w=256&q=75)
%2F300x300%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fsuccessful-fishing-expedition-maryland-2626.jpg&w=256&q=75)
%2F300x300%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fstellar-striped-bass-haul-md-2583.jpg&w=256&q=75)
%2F300x300%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fbest-striped-bass-fishing-oxford-2759.jpeg&w=256&q=75)
%2F300x300%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fsuccessful-fishing-oxford-2583.jpg&w=256&q=75)
%2F300x300%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Ffishing-adventure-oxford-2444.jpg&w=256&q=75)
Scenic Chesapeake Bay Fishing | Maryanne Charters
What you will be catching:
 Black Drum
Black Drum Bluefish
Bluefish Sea Trout
Sea Trout Spanish Mackerel
Spanish Mackerel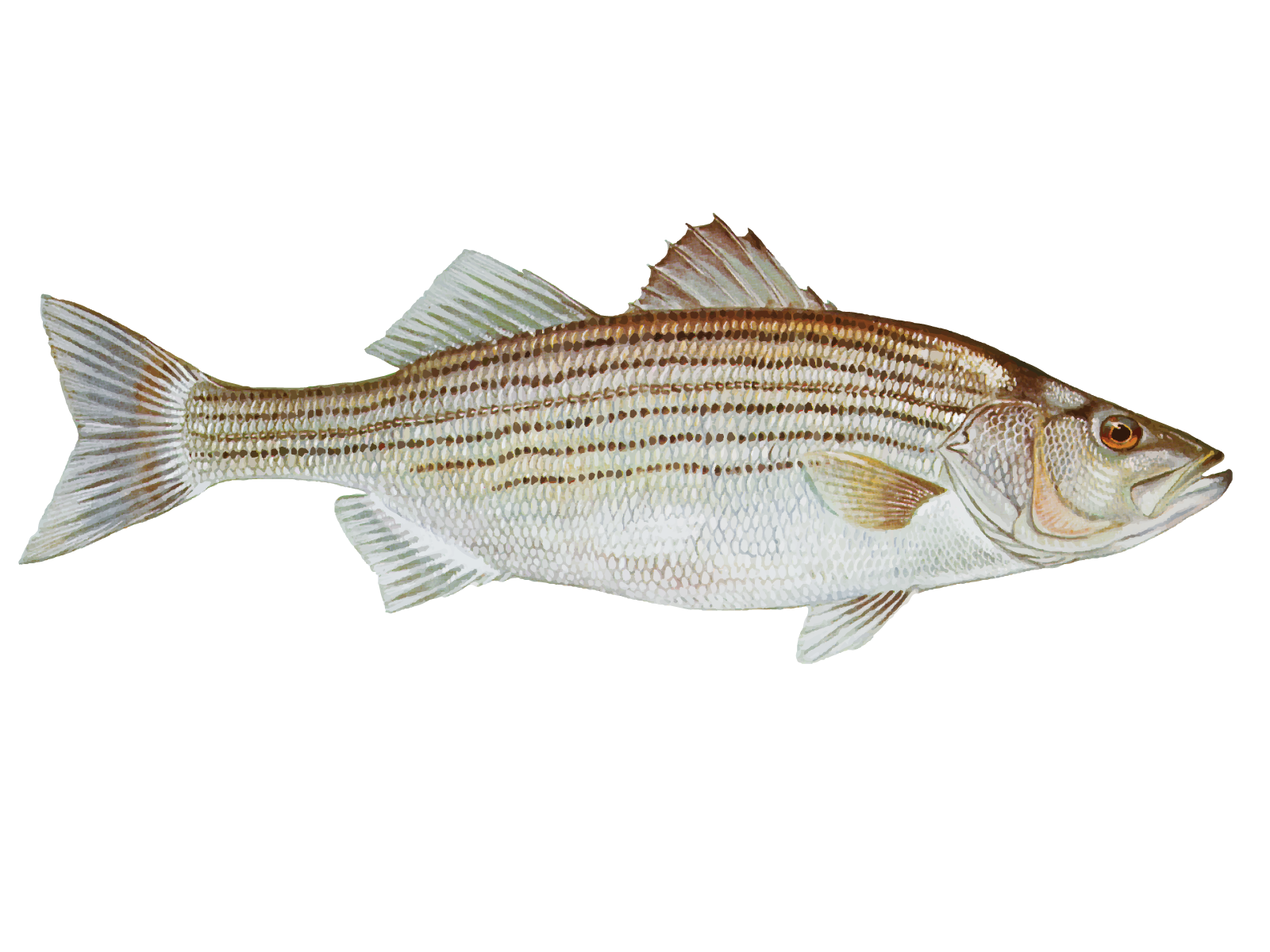 Striped Bass
Striped Bass
- 7-hour scenic Chesapeake Bay cruise with light fishing
- Target Spanish Mackerel, Striped Bass, Black Drum, and Bluefish
- Relaxed family-friendly experience with wildlife viewing opportunities
Trip Pricing and Availabilities :
Trip pricing information is temporarily unavailable.
Chesapeake Bay's Ultimate Fishing Cruise
Hey there, fellow fishing enthusiasts! Ready for a day on the water that's as laid-back as it is exciting? Captain Gary Bramble here, inviting you aboard the Mary Anne for a full day of fishing and cruising in the beautiful Chesapeake Bay. This isn't your typical high-pressure fishing charter – we're talking about a relaxed 7-hour trip where you can wet a line, soak up the scenery, and maybe even spot some wildlife along the way. Whether you're an seasoned angler or just looking to try your hand at fishing while enjoying a day on the bay, this trip is tailor-made for you.
What's the Deal?
Picture this: You're cruising along the calm waters of Chesapeake Bay, rod in hand, with the sun warming your face and a gentle breeze keeping things comfortable. That's what we're offering here – a perfect mix of light fishing and scenic cruising. We'll be targeting a variety of species including Spanish Mackerel, Striped Bass (or "stripers" as we call 'em around here), Black Drum, Bluefish, and Sea Trout. But don't worry if you're new to fishing – Captain Gary's got you covered with all the gear and know-how you'll need. The Mary Anne is set up for comfort, so you can kick back between bites and just enjoy being out on the water. It's the kind of day that's perfect for small groups, couples, or families looking to spend some quality time together without the pressure of a hardcore fishing expedition.
How We Roll on the Water
On this trip, we keep things simple and effective. We'll be doing a mix of trolling and light casting, depending on what the fish are biting. Trolling is great because it lets us cover more water and increases our chances of finding the fish. We'll set up a spread of lines behind the boat, each rigged with lures or bait that are irresistible to our target species. As we cruise along, these lures dance in the water, mimicking the movement of baitfish. When a fish strikes, you'll hear that sweet sound of the reel singing – that's when the real fun begins! For those who prefer a more active approach, we'll also do some casting. I'll show you the hotspots where fish like to hang out – structures, drop-offs, and areas where bait tends to school up. We use light to medium tackle, which gives you a good feel for the fight without being too heavy for a day of casual fishing. And don't sweat it if you're new to this – I'm here to guide you through every cast and reel.
Species You'll Want to Hook
Spanish Mackerel: These speedsters are a blast to catch and even better to eat. They're known for their lightning-fast runs and acrobatic jumps when hooked. We typically see them from late spring through early fall, with the peak being in the summer months. They're not huge – usually 2-4 pounds – but what they lack in size, they make up for in fight and flavor. When we're trolling for Spanish Mackerel, keep an eye out for birds diving – that's often a sign that these fish are feeding on the surface.
Striped Bass (Rockfish): The crown jewel of Chesapeake Bay fishing, stripers are prized for their size and the challenge they present. These fish can range from schoolies of a few pounds to trophy-sized monsters over 40 pounds. We target them year-round, but the spring and fall runs are particularly exciting. Stripers love to hang around structure, so we'll often fish near bridge pilings, rocky points, or over oyster beds. There's nothing quite like the thump of a big striper hitting your lure – it's a feeling that keeps anglers coming back year after year.
Black Drum: These bruisers are the gentle giants of the bay. Black Drum can grow to over 80 pounds, though we more commonly catch them in the 20-40 pound range. They're bottom feeders with a soft spot for crabs and clams. We typically target them in the spring and early summer when they move into the bay to spawn. Fishing for Black Drum is all about patience and feel – you need to detect their subtle bites and set the hook just right. But when you hook into one, hold on tight! They pull like a freight train and will give you a workout you won't soon forget.
Bluefish: If you're looking for pure, aggressive action, Bluefish are your target. These toothy predators are known for their savage strikes and relentless fights. We see them most often from spring through fall, with the biggest ones (called "choppers" by locals) showing up in the late summer and fall. Bluefish are voracious eaters and will hit just about any lure or bait you throw at them. They're great fun on light tackle, and their aerial acrobatics when hooked will have you grinning from ear to ear.
Sea Trout (Weakfish): Last but not least, we have the Sea Trout, also known as Weakfish. Don't let the name fool you – there's nothing weak about the fight these fish put up. They're known for their beautiful, speckled coloration and their tender, flaky meat. We typically catch them in the 2-5 pound range, though bigger ones aren't uncommon. Sea Trout are most active in the warmer months, from late spring through early fall. They love to hang around grassy areas and drop-offs, and they're suckers for soft plastic lures or live bait. When you hook one, you'll be treated to a series of head shakes and short runs that'll keep you on your toes.
Why Folks Keep Coming Back
You know, it's not just about the fish – though that's a big part of it. What really makes this trip special is the whole package. You're out here on the beautiful Chesapeake Bay, with its rich history and diverse ecosystem. As we cruise along, you might spot ospreys diving for fish, or see a pod of dolphins playing in our wake. The scenery is always changing, from the rugged shorelines to the open waters. And there's something about being on a boat that just helps you unwind and forget about the daily grind for a while. Add in the chance to catch some fish, learn new techniques, and maybe bring home dinner, and you've got yourself a day that's hard to beat.
Time to Get on Board
So there you have it, folks – a full day of fishing and cruising that's perfect for anyone looking to enjoy the best of Chesapeake Bay. Whether you're an experienced angler or someone who's never held a rod before, this trip has something for you. We provide all the gear, the know-how, and a comfortable boat to enjoy it all from. All you need to bring is your sense of adventure and maybe a cooler for your catch. Remember, the bay is always changing, so no two trips are ever the same. That's what keeps it exciting! So why not grab some friends or family and join us for a day on the water? The fish are biting, the scenery is stunning, and the Mary Anne is ready to sail. Give us a call or book online – we can't wait to show you what Chesapeake Bay fishing is all about!
Learn more about the species
Black Drum
## Black Drum (Pogonias Cromis) ## Black Drum Description The Black Drum is a fish in the Sciaenidae family. The Black Drum is also the largest fish of that family, including almost 300 species, including their popular cousin, the Redfish. They are known as drums or croakers due to the repetitive drumming or croaking sounds they make. They are black and or grey and have powerful jaws with strong teeth capable of crushing prey like shellfish and oysters. ## Black Drum Size The Black Drum's typical weight range varies considerably from 5 to 30 pounds but can reach a weight of up to 90 pounds. If you intend to eat your catch, you may want to release Black Drum over 15 pounds. As they grow larger, the meat is tough and more comparable to chicken than a flaky texture. Also, the flavor of the older fish is not as tasty as the smaller-sized fish. ## Black Drum Spawning Black Drum have mating calls that they use to seek out others during the spawning season, capable of producing tones that reach 100 to 500 Hz. Black Drum grow rapidly and reach maturity within the first 2 years of their lives and live to 50 years. The females can lay eggs every three days during the spawning season. Their spawning seasons vary due to location, spawning occurring in February and March in southern areas like Texas, and April to June farther north. ## Black Drum Habitat Black Drum typically prefers brackish waters and estuaries. The adults live closer to the saltier areas near the ocean. They can be found around an oyster bed and other areas with plentiful food sources. The juveniles prefer the less salty areas of the same estuaries with sandy bottoms. Black drum are extremely adaptable when it comes to temperatures and salinity and can be attracted to freshwater creek openings and extremely shallow water, but are also found in depths of up to 100 feet. ## Black Drum Fishing You will find the best Drum fishing is on shallow water, muddy flats, and oyster beds, but they can also be found near inlets, pier pilings, creeks and estuaries that make way inward. Most anglers also fish for the Black Drum in the spring around the spawning season. At this time, the fish school up and are easier to target. After the spawning season, the fish disperse and become much harder to target. ## ## Black Drum Bait and Lures The best bait an angler can use for Drum fishing is live bait because they are bottom-feeders. Live bait such as fresh soft crabs, mollusk, peelers crabs, sea clam, or crushed mussels are the preferred bait. Anglers like to use crab because it does not tend to get eaten by catfish and other bait stealers. If you are not using live bait, then choose very slow-moving jigs like bucktail jigs. It is also vital to use the correct weighting for the conditions to ensure that your bait is on the bottom. When fly fishing, most anglers prefer to use a 7- or 9-weight fly rod, leaning towards a 9-weight for throwing heavier flies and a little extra strength when pulling on fish that may be more than 20 pounds. You will want to present your fly on the bottom, and weighted black flies that get to the bottom quickly are best such as the Redfish Worm, Merkin, and Clouser Minnow. ## Distribution and Range The Black Drum has a wide range and extends as far north as Nova Scotia, down the whole Atlantic coast of the United States, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico. ## Black Drum Regulations Check the state you are fishing in as they each have their own regulations, but you will find most at 5 fish per day between 14 and 24 inches long, with one allowed over 24 inches.

Bluefish
Bluefish (Pomatomus saltatrix) Fish Description
Bluefish is a common game fish that is known for its delicious taste. Bluefish is a warm-water migratory species living in the Atlantic Ocean from Nova Scotia to Argentina and Spain to southern Africa. In South Africa, the Bluefish is known as Shad or Elf; in New Zealand and Australia, it is called Tailor. Bluefish are seasonal visitors to Cape Cod waters, arriving in mid-June and remaining until mid-October. They spend the winter in warmer waters from North Carolina to Florida's tip.
The Bluefish has a moderately proportioned body; one of its distinctive features is its broad and corked tail and its spiny first dorsal and pectoral fins that are usually folded back in a grove. The Bluefish is generally grayish to blue-green in its dorsal area, whereas its belly and lower sides fade to white.
It is a voracious predator with a large mouth and flat, triangular teeth that are strong, sharp, and prominent teeth.
Bluefish Diet
As aggressively strong feeders, the Bluefish have a complex menu of prey. They can chase after schools of forage fish owing to their fast swimming speed. They usually go on a feeding frenzy by attacking these schools of fish even after having satisfied their stomachs. They especially like sardine-like fish, Menhaden, Weakfish, Grunt, Anchovy, Squid, and Shrimp. In return, the Bluefish serve as food for bigger fish like Dolphin, Billfish, Sharks, and Tuna, among others.
Bluefish Size
Commonly, the Bluefish can grow up to 7 inches; they weigh up to 40 lbs. However, most of the Bluefish population reaches only up to 20 lbs.
Interesting Facts About the Bluefish
- The Bluefish is the only remaining living species from the Pomatomidae family. It used to be grouped with Gnomefish, but the latter were separated.
- Lophar miocaenus from Southern California is an extinct relative of the Bluefish from the Late Miocene Period.
- Bluefish are reported to live up to 9 years.
- The Bluefish are cannibalistic, and they sometimes eat their own young.
- The Bluefish are known for churning water like a washing machine, attacking schools in shallow depths. This is called “Bluefish Blitz.”
- Bluefish is a common host to many parasites; in particular, it is often inhabited by the parasite named Philometra saltatrix, which is found in the ovaries of the fish.
- Despite being high in omega-3, children and adult women are warned against consuming Bluefish due to its significant mercury content.
- When properly prepared, bluefish is extremely good to eat, with mild, flaky meat, though larger fish (those weighing more than 10 pounds) have a stronger flavor than their smaller brethren.
Bluefish — Fishing Techniques
To reel in lots of Bluefish, you can use the following harvesting methods: trawls, hook and line, and gillnet. Note that you can only use a circle hook and nothing else; recreational anglers can only capture up to three pieces of Bluefish per day (no minimum size). As for artificial lures or flies, you can use only up to a maximum of two treble hooks. Be careful when handling Bluefish since they can bite you, leading to some serious wounds. Oily fish, such as eels, make excellent bait for bluefish. However, almost any type of baitfish can be used. When learning how to catch bluefish, another option is to use cut bait. Try chunks shaped like a small lure.
You can best fish for Bluefish from tidal rivers, bays, and sandy harbors during summer. In late summer, small, juvenile bluefish known as "baby blues" or "snappers" can be caught in sandy harbors, bays, and tidal rivers. This is an excellent fish for young and inexperienced anglers to catch. Bluefish are frequently caught using gillnets in the commercial bluefish fishery, but they can also be nabbed using a hook, line, or trawl gear.
A permit must be secured to catch Bluefish in commercial fisheries. Some states also impose a specific catch limit for commercial and recreational fishing.
Bluefish Habitat and Distribution
As a marine pelagic fish species, the Bluefish generally inhabit subtropical and temperate waters all around the globe. Most thrive along the continental shelves of America (except in northern South America and south Florida), Australia, and Southeast Asia. Interestingly, the Bluefish is also not found on the north side of the Pacific Ocean.
Typically, anglers find school of Bluefish in various habitats, including brackish waters, estuaries, rock headlands, surf beaches, or above the continental shelf. From time to time, the Bluefish migrate to open waters in schools.
Bluefish fishery management employs a bag limit for recreational fishing and an annual quota distributed to states for commercial fisheries to avoid overfishing.

Sea Trout
Sea Trout (Salmo trutta) Fish Description
Also known as Spotted Sea Trout or Speckled Trout, Sea Trout are anadromous, meaning they migrate from the sea to spawn in freshwater.
The most distinct feature of Sea Trout is their torpedo-shaped (fusiform) and elongated body. They are similar to brown trout but have a much more silvery appearance. They have an adipose fin which is a feature present in all species of trout. They have numerous spots all over the body.
This fish closely resembles the Rainbow Trout and Atlantic Salmon. What makes it different from the others is that the rainbow trout possess black spots on its tail, whereas the Atlantic Salmon has no red tinge on its adipose fin.
Sea Trout Diet and Size
Sea Trout love to feast on shrimps, prawns, small crabs, and fish. They also feed on zooplankton and zoobenthos.
Adult Sea Trout can grow from 14 to 24 inches long and weigh a little over one pound to 5 pounds. Some Sea Trout were found to have weighed up to 40 pounds in certain instances.
Interesting Facts About the Sea Trout
- As an anadromous fish species, the Sea Trout shares this characteristic with the Sea Lamprey, Striped Bass, and Salmon.
- Some salmonids like the Cutthroat Trout (Oncorhynchus clarkii), Arctic Char (Salvelinus alpinus alpinus), Coho Salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch), Dolly Varden (Salvelinus malma), and Brook Trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) are also commonly called Sea Trout.
- Male Sea Trout who are in breeding season develop a skype, which is a hook-like protrusion on their lower jaw.
- When in freshwater, Sea Trout are olive in color, whereas they are silvery when they are in salt water.
- Young Sea Trout remain in freshwater for almost five years before going back to sea; during this journey, they can travel up to 40 kilometers in a day.
- The Sea Trout is considered the first fish to have undergone artificial reproduction; the pilot activity is said to have occurred in 1739 in Germany.
Sea Trout — Fishing Techniques
Sea Trout are considered common table fare; they are usually processed and frozen. Because of this, this species has become popular among commercial fishers. Freshwater anglers basically catch Sea Trout via fly fishing.
Commercial anglers usually use spinners, lures, and live bait like herring and mackerel strips dipped into the water reaching the sea bed. Since Sea Trout are good fighters who always like to bait, you are recommended to utilize artificial lures; the most effective are jerk baits, topwater plugs, plastic shrimp, spoons, and plastic tail grub jigs.
When sea trout fishing, look for them in grass flats or shallow waters at night. If you have a hard time, you can try trolling at idle speed along these areas. Remember that during winter, Sea Trout form big schools and are usually found in waters as deep as 164 feet.
Considered one of the most highly rated fish, the Sea Trout is prized among anglers. In some countries like Germany, however, this species is protected and highly regulated.
Is Sea Trout Good to Eat?
Sea trout or Speckled trout is a popular game fish found in many coastal areas worldwide. One question often arises is whether sea trout is good to eat. It's important to understand that sea trout can vary significantly in taste depending on where they were caught and what they've been feeding on. Generally speaking, sea trout has a mild and delicate flavor that many people find appealing. Additionally, because sea trout are typically smaller than other salmonids like salmon or steelhead, their flesh tends to be more tender and less oily.
Speckled Trout are a tasty fish that is very good to eat with moderate-flaky, white meat. It is softer than other inshore fish, so it is important not to overcook it, or it will become very mushy.
Regarding nutrition, sea trout is an excellent source of protein and omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients have been linked to various health benefits, including improved brain function and heart health.
Sea Trout Habitat and Distribution
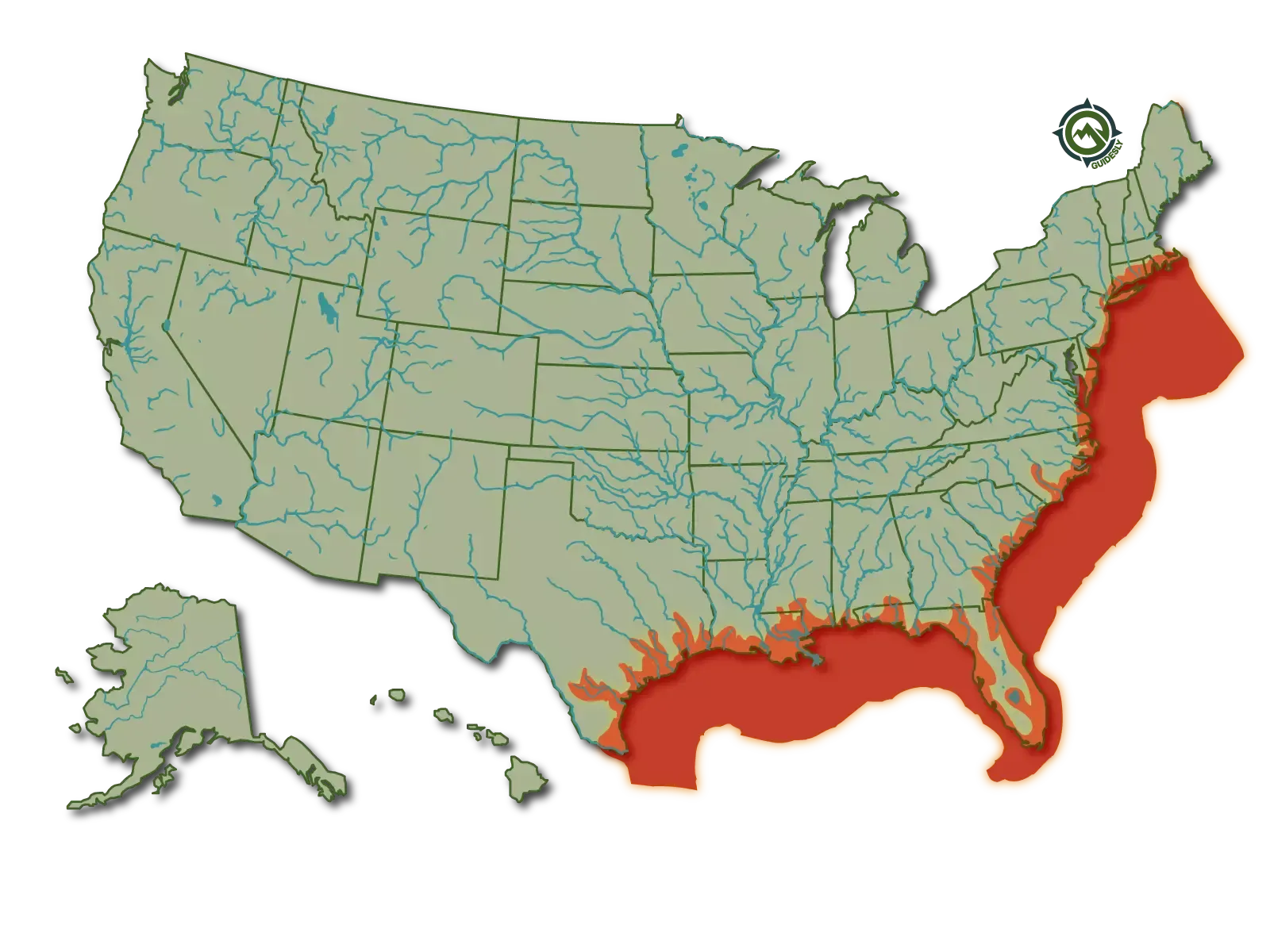
Sea Trout thrive best in cold lakes and rivers (they like temperatures between 33.8 to 80.6°F); they spawn on the gravel bottoms of streams and rivers. They usually spawn in November to December. Sea trout in South Carolina typically live in estuaries all year, but they may congregate to overwinter in deeper channels and rivers or the main estuary, potentially increasing fishing pressure.
Sea Trout have vast and fairly distributed populations in Europe, especially along the coasts of Iceland, the UK, and the Atlantic and Baltic areas. They are abundant in the Caspian and Black Seas but are not present in the Mediterranean. Certain populations of Sea trout have also been reported in the US, particularly in the Canadian rivers, Columbia River, and the Atlantic and Pacific coasts.

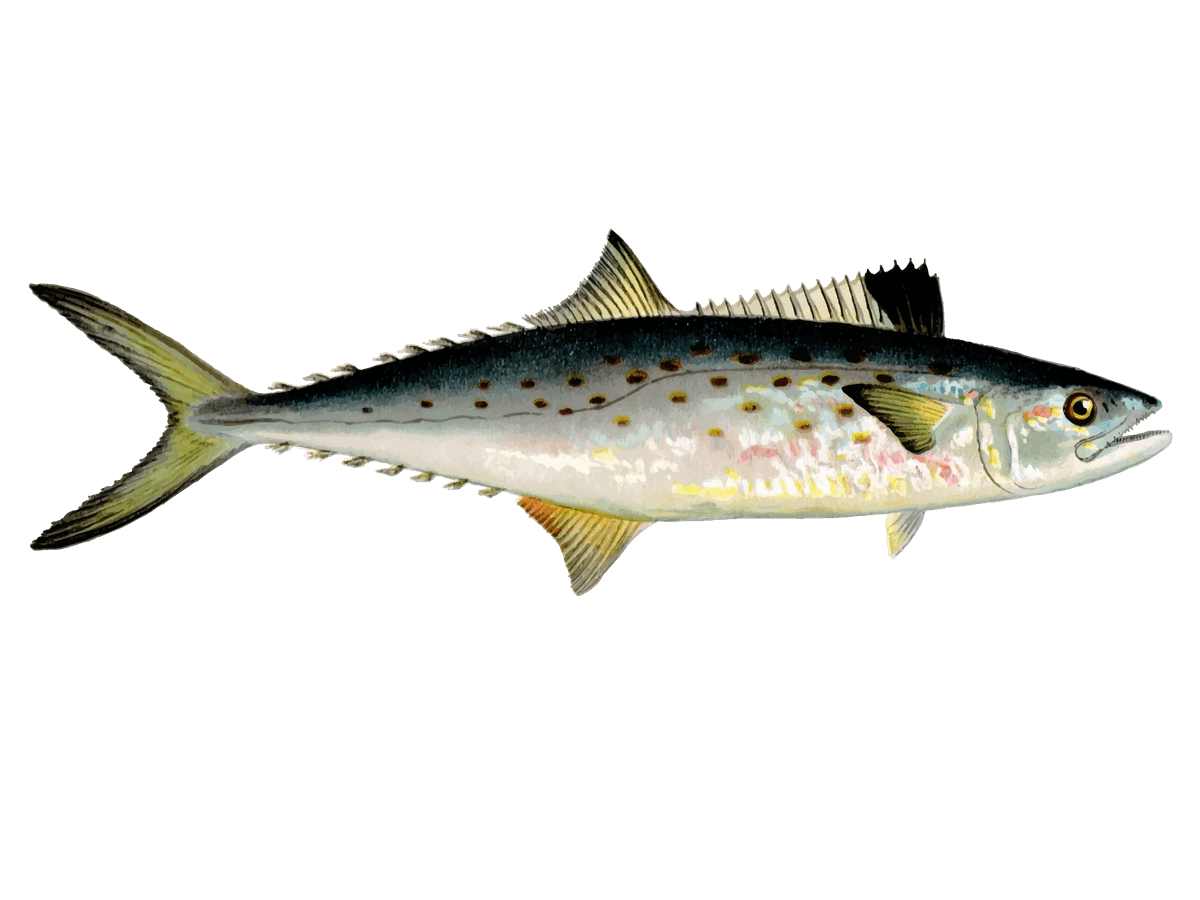
Spanish Mackerel
Spanish Mackerel (Scomberomorus maculatus)
Often found both coasts of Florida and the Gulf of Mexico, the Spanish Mackerel (Scomberomorus maculatus) is a favorite fishing target for both recreational and commercial fishers. It can be easily identified with its long, streamlined body, silvery color with a dark greenish top, and yellowish oval spots scattered on its sides. They are speedy swimmers and can often be seen in large groups or schools. They also migrate from the northern part of the Atlantic coast to as far south as Mexico during winter. They can, however, be found in pretty much every ocean in the planet.
Spanish Mackerels are carnivores and usually prey on prey mainly on herring, menhaden, sardines, mullet, needlefish, and anchovy and, sometimes, even on shrimp, crabs, and squid. On the other hand, same as their close relatives like tuna and other mackerels, they are preyed upon by dolphins, sharks, and of course, humans.
The Spanish Mackerel is a highly valued fish for both sports fishers and commercial fishers because of its tasty meat that can be cooked by grilling, frying, baking, and even by smoking. It’s also a popular fish in Japan and other countries as it can be eaten raw as sushi.
Interesting Facts About Spanish Mackerel
- The biggest Spanish Mackerel ever caught measures a little over six feet long and weighs about one hundred and twenty pounds.
- Angler Doug Buhagiar with the help of his brother caught the humongous fish on the beach on Fraser Island off Australia’s eastern Queensland coast.
- Spanish Mackerels are one of the fastest swimmers in the ocean, clocking at about 5.5 meters per second on average.
- They swim in large groups or schools that can stretch up to 20 miles.
- They can live up to twenty-five years in the wild.
- As with other mackerel species, Spanish Mackerels are often caught for food.
- They can be cooked in various methods, including: baking, grilling, steaming, smoking, poaching, and frying.
- The Spanish Mackerel is also a popular sushi fish.
- They are a source of omega-3 fatty acids in human diet.
- High human consumption meant high demand for the fish, thus, led to overfishing and a significant fish population decline over the past few decades.
- Fishing restrictions were made to help repopulate oceans with this particular fish species.
- Annual catch limits are divided between the commercial and recreational fishers in both the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico.
- Minimum size restrictions are also placed to provide the species time to mature and spawn.
- Since the regulations, Spanish Mackerel populations have significantly improved.
- Females can lay 500,000 to 1.5 million eggs throughout the spawning season.
- Their eggs float in the water because they contain oily drops.
- For fertilization, the eggs merge with sperm cells that are released by males.
Spanish Mackerel Average Speed and Size
Clocking in on average at 5.5 meters per second, the Spanish mackerel is one of the fastest and most agile fish species in the ocean. They can also mature and grow really fast, reaching their full maturity in just two years. An adult measures about one to two feet in length and weighs around eight to eleven pounds.
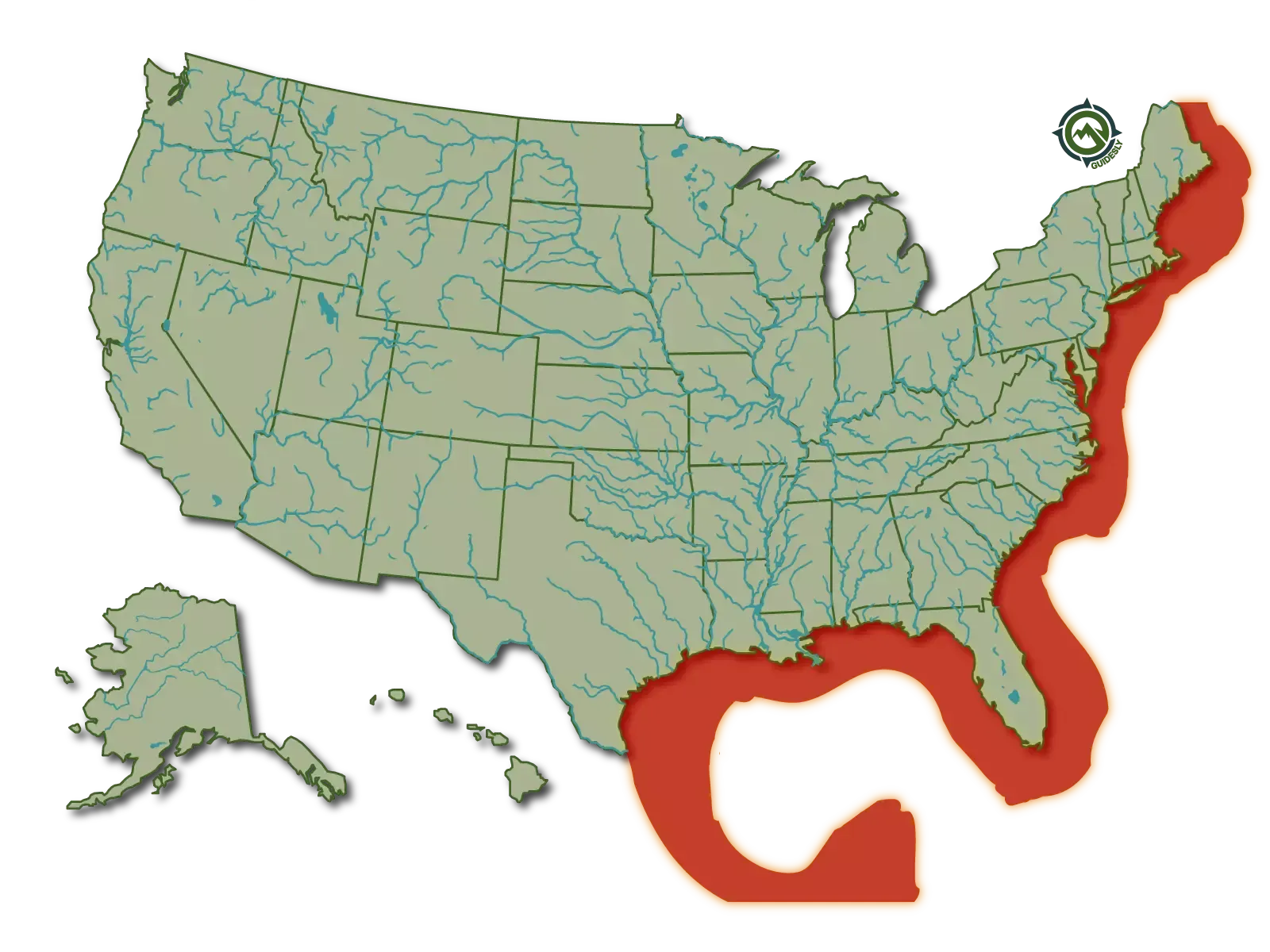
Where to Find Them
Many successful anglers have caught Spanish Mackerels by trolling or drifting on boats. Others have also been successful fishing on piers, jetties, and beaches by casting spoons and jigs and live-bait fishing. They can often be found in large schools swimming near the surface of the water. Although, this fish live mainly in tropical and subtropical waters, it can sometimes be seen in temperate waters as well.
Spanish Mackerel Fishing Tips
If you’re going to be fishing offshore, look around structures in the open waters where schools of Spanish Mackerels are often seen. Just make sure to drift to the area where they are so as not to spook the school of fish away. For nearshore fishing, again check around structures in open waters, including flats and oyster bars. In a warmer weather, schools are often spotted closer to shores. So you might want to stay on land and fish in the surf, piers, and jetties when the water warms.
As for the gears you’re going to need, here are some of our recommendations:
Equipment
- Light to medium spinning tackle
- Medium 7 to 8-foot rod
- 12-20 lb. braided line
- 1/0-2/0 circle hook that matches bait size
Lure
- Heavy metal lures, shiny spoons
- Plastics with jig heads
Bait
- Live shrimp and fish such as sardines, minnows, mullet, and greenbacks
- Cut bait such as squid
Is Spanish Mackerel Good to Eat?
When it comes to delicious fish that is versatile in flavor and texture, Spanish Mackerel is at the top of the list. This fish is a great ingredient to cook with and offers many different options for tasty dishes. It has a mild flavor that is not too fishy. When cooking with Spanish Mackerel, it can be grilled, baked, or even smoked, which makes it an excellent choice for different cuisines. The texture of this fish is also quite unique, as it is both flaky and tender at the same time. Whether you want to fry it up for a crispy meal or use it in a stew, there are many possibilities when it comes to preparing Spanish Mackerel.
Besides being a delicious and versatile fish, Spanish mackerel is also a healthy option for your diet. It is packed with essential nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids and protein, which can improve heart health and provide energy.

Striped Bass
Striped Bass (Morone Saxatilis) Description
The Striped Bass (Morone saxatilis), or Atlantic Striped Bass, Stripers, or Linesider, is a popular game fish for recreational and commercial fishers. As the name suggests, it has seven to eight stripes running down the sides of its body; its color can vary from light green and olive to brown and black. It also has a shimmering white belly and plump bodies that can grow as heavy as 70 pounds and as long as 5 feet, making it easily distinguishable from other species.
Although this fish mostly lives in saltwater during its adult life, it’s anadromous as it spawns (and is even known to adapt well) in a freshwater environment.
It can naturally be found along the East Coast (from as far north as Canada to down south in the Gulf of Mexico). However, you can find it in most water bodies in North America as the species was introduced across the continent for recreational fishing and for controlling the gizzard shad population, which the Striped Bass is known to prey upon.
Interesting Facts
Striped Bass spawn in freshwater and many of the Stripers become landlocked because of dams and other human-made obstructions; but, as earlier mentioned, they adapt well and can thrive in a freshwater habitat.
If you’re fishing for food, the Striped Bass is excellent for eating not only for its plump and meaty body but also for its exquisite, sweet taste, similar to its close relative, the Black Sea Bass.
Striped Bass Size and Speed
For those of you who are planning to fish for this species, yes, they are known to be powerful swimmers, but they’re not particularly fast, making them reasonably easy to catch. Although they can grow much bigger, most caught weigh around twenty to forty pounds.
Where do Striped Bass Live?

You can fish for Striped Bass pretty much any time of the year and can find them in nearly every body of water in the United States. It’s also worth noting that the Chesapeake Bay, Maryland is the major producer while the Hudson River in New York and New Jersey is the second.
However, if you’re on the West Coast, you may want to try your luck in the San Francisco Bay and the surrounding coastline. Colorado rivers and lakes such as Lake Havasu, Lake Mead, Lake Powell, Lake Pleasant, and Lake Mohave are also known to have a great abundance of Striped Bass.
Striped Bass is a structure-oriented fish meaning they can be found around physical structures such as coral reefs, sand bars, and drop-offs. They stay at the bottom of the ocean along the shores as it looks for food. And because they love to swim in moving waters, you can most locate Stripers within yards of the shorelines.
Striped Bass Migration
One of the most exciting aspects of striped bass is their annual migration patterns. These fish are known to migrate long distances, sometimes thousands of miles, which makes them a fascinating subject for study. Striped bass prefers moderate temperatures between 55° F and 68° F. To stay within this temperature range, most striped bass migrate up and down the Atlantic coast from spring to fall.
Scientists have been studying striped bass migration for many years, and they have discovered that these fish travel from estuaries to the open ocean and back again each year. Striped bass can migrate up to 2,000 miles during their lifetime! They typically move northward in the spring and summer months when water temperatures warm up, then head south towards warmer waters in the fall.

The spring striped bass migration begins from the deeper waters off the Virginia and North Carolina coasts. In the spring, the stripers start their northern migration stopping to spawn in the rivers, estuaries, and bays such as the Delaware River, the Hudson River, and the Chesapeake Bay. The Stripers continue north and eventually spend their summers in the cool waters in New England, and sometimes further North to Canada.
The striper migration bait typically begins in the fall as the water cools. If you want to experience this unique opportunity, you'll want to head for one of the most amazing events that an angler can experience. Striper bait, including pogies, peanut bunker, and silversides, will come out of bays and into the ocean early. The hungry stripers want to fatten up for the cold season as winter approaches, so they're actively searching out prey. Stripers seek out the enhanced bait pods that create feeding frenzies. Look for baitfish volcanoes erupting from the water or birds signaling the wounded baitfish. If you are truly fortunate, you will see whales coming from below the baitfish volcano. Fall migration continues all the way until December around the New Jersey coast and parts of January in the Virginia region.
Check out this detailed Striped Bass Migration article.
Is Striped Bass Good to Eat?
Striped bass, also known as "striper," is a popular saltwater fish that can be found along the Atlantic coast of North America. Many people wonder if striped bass is good to eat, and the answer is yes! Striped bass is not only delicious but also packed with nutrients that can benefit your health.
One of the benefits of eating striped bass is its high omega-3 content. Omega-3s are essential fatty acids that help reduce inflammation in the body, improve brain function, and even lower your risk of heart disease. Striper meat contains about 0.5 grams of omega-3s per 100 grams, making it an excellent nutrient source. Additionally, striped bass is rich in protein - a crucial component for building and repairing tissues in your body. A serving size of just 100 grams provides approximately 20 grams of protein.
Fishing Techniques - How to Catch Striped Bass
Striped Bass can be caught year-round and in almost any condition; you can, however, increase your chances if you know exactly what, when, where, and how to look. Stripers are known to swim around and feed in moving waters, near structures along the shores, and you will find them where the water is cooler near the surface during dusk and dawn. Cast your lines out early or late in the day from bridges, piers, bulkheads, or even while wading in the surf.
Choosing the Right Bait
Striped Bass are mostly finicky predators being picky about the baits they will take. It’s best to use live baits such as herring, menhaden, mackerel, eels, squid, anchovies, bloodworms, or shad as it will help attract them with the live bait’s movement.
Choosing the Right Equipment
Although you can use almost any rod and reel for Striped Bass fishing, you can be more successful using rods that are 8 to 14 feet in length, especially for fly fishing. You should use a thinner and more sensitive yet stronger line with little stretch like a braided line. If you prefer using the monofilament type, make sure that it’s strong enough to withstand up to 20 pounds of weight as these fish are not only big, heavy fish, but also strong fighters.
Find fishing tips, techniques, and the best destinations for Striped Bass Fishing
Why are Striped Bass Called Striper?
Striped bass, or Morone saxatilis, is a popular game fish native to the Atlantic coast of North America. It is widely known as "striper," which begs the question: Why do they call striped bass striper? The answer to this question lies in the distinct markings on the fish's body.
The name "striped bass" comes from its characteristic stripes running along its sides. These stripes are typically seven to eight in number and run from just behind the gills to the base of the tail. When viewed from afar, these stripes can appear like bars or lines that make up a striped pattern on their silver-green skin.
Given that this species has such distinctive vertical stripes, it makes sense why they are called stripers. The name has become so widely used among anglers and fishing enthusiasts that it is now more common than calling them by their scientific name.
What is the Hybrid Striped Bass?
Hybrid striped bass is a popular fish species among anglers and seafood enthusiasts. As the name suggests, it's a crossbreed between two different types of bass: striped and white. The hybridization process has resulted in a fish with desirable traits such as rapid growth, aggressiveness, and resistance to diseases and parasites.
Hybrid striped bass can grow up to 30 inches in length and weigh as much as 15 pounds. They have streamlined bodies with dark stripes running along their sides, which give them an attractive appearance. Moreover, these fish are known for their delicious taste and versatility in cooking methods.
Due to its popularity, hybrid striped bass is widely farmed across several regions in the United States. It's commonly used by chefs in various dishes such as sushi rolls, grilled fillets, or stews.
Striped Bass Population
The wild striped bass population is an essential aspect of marine fisheries conservation efforts. Striped bass are a popular game fish that attract recreational anglers from all over the world. Stripers also play an essential role in the natural resources ecosystem in the Atlantic Ocean and the many tributaries like Delaware Bay, Delaware River, Hudson River, and many coastal rivers. Striped bass are a top predator in many coastal habitats, feeding on smaller fish and crustaceans.
Unfortunately, the striped bass population has been under pressure for several decades due to overfishing and habitat loss. One of the primary conservation efforts underway is the implementation of regulations aimed at protecting striped bass populations from overfishing. This includes restrictions on fishing methods and gear, as well as limitations on catch limits for both recreational and commercial fishermen. Additionally, many states have implemented size limits for the fish that can be caught to allow younger fish to reach their reproductive age.
Despite these efforts, the future of the striped bass population remains uncertain. Climate change is causing significant shifts in ocean temperatures and currents that could impact the availability of prey species for striped bass.
A Few Striped Bass Resources:
-Striped Bass Migration, article tracking the Striped Bass Atlantic Coast migration
-Striped Bass Lures, expert guides weigh in with the best striped bass lures
-Striped Bass Bait, top 10 striped bass baits
-Striped Bass Cape Cod, expert guide talks about catching striped bass on Cape Cod
-Striped Bass Chesapeake Bay, expert guides talk about catching striped bass on Chesapeake Bay


About the Robbins (Pilothouse)
%2F%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fvehicle_picture%2Fboat.jpg&w=1200&q=75)
Vehicle Guest Capacity: 6
Manufacturer Name: Cummins
Maximum Cruising Speed: 32
Number of Engines: 1
Horsepower per Engine: 500
Step aboard the Mary Anne for a laid-back day on Chesapeake Bay. This 7-hour trip blends easy fishing with scenic cruising, perfect for those who want to unwind on the water. You'll have chances to reel in Spanish Mackerel, Striped Bass, Black Drum, and Bluefish while taking in the bay's natural beauty. Captain Gary Bramble provides quality gear and a comfortable boat setup that's ideal for small groups of up to 6 guests. Expect a smooth ride with opportunities to spot local wildlife as you explore the coastline. Whether you're a couple seeking a peaceful outing or a family looking for a fun day trip, this cruise offers a relaxed atmosphere and just the right mix of fishing and sightseeing. It's a great way to experience the charm of Chesapeake Bay without any pressure – just good times on the water.
%2Ffit-in%2F250x250%2Fguide_websites%2F11704%2Fimages%2Fmaryanne.png&w=1200&q=100)


%2Ffilters%3Aformat(webp)%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fstellar-striped-bass-haul-md-2583.jpg&w=768&q=75)
%2Ffilters%3Aformat(webp)%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fbest-striped-bass-fishing-oxford-2759.jpeg&w=768&q=75)
%2Ffilters%3Aformat(webp)%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fsuccessful-fishing-oxford-2583.jpg&w=768&q=75)
%2Ffilters%3Aformat(webp)%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Ffishing-adventure-oxford-2444.jpg&w=768&q=75)
%2Ffilters%3Aformat(webp)%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fstriped-bass-fishing-oxford-2678.jpeg&w=768&q=75)
%2Ffilters%3Aformat(webp)%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fsix-bluefish-oxford-fishing-2624.jpeg&w=768&q=75)
%2Ffilters%3Aformat(webp)%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fstriped-bass-fishing-md-2633.jpeg&w=768&q=75)
%2Ffilters%3Aformat(webp)%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fstriped-bass-fishing-oxford-2701.jpeg&w=768&q=75)
%2Ffilters%3Aformat(webp)%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Ffishing-adventure-oxford-2495.jpeg&w=768&q=75)
%2Ffilters%3Aformat(webp)%2Fusers%2F33f546a2-b1e8-4c31-a92a-6c27aa2608c8%2Fimages%2Fsuccessful-fishing-expedition-maryland-2626.jpg&w=768&q=75)
